Two Sum Solution in Python 3 [LeetCode 1]
Given an array of integers nums and a target integer.
Return the indexes (not values) of the 2 numbers that add up to the target value. One solution and one element can’t be used twice.
Example
- nums = [1,2,8,7,11,15], target = 13
- output= [1,4], indexes start at 0
- index 1 = value 2 and
- index 4 = value 11
- 2+11 = target
Analisys
Use a dictionary to keep track of the indexes and values that are already processed.
Loop thru each item of the nums list and if the current item is found in seen, return the index of the seen number and the current index. If it’s not found yet, add it in seen dictionary as:
- the target – the current number aka the difference and
- the current index.
If the loop is finished without returning anything return an empty list.
Test Code
def main():
print("Python test")
nums = [1,2,8,7,11,15]
target = 13
print("input: nums= " + str(nums))
print("input: target= " + str(target))
s = Solution()
result = s.twoSum(nums,target)
print("result: " + str(result))
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: list[int], target: int) -> list[int]:
"""
2021 Dragos Ion
Two Sum using seen list
"""
seen = {}
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] in seen:
return [seen[nums[i]], i]
else:
seen[target - nums[i]] = i
i+= 1
return []
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()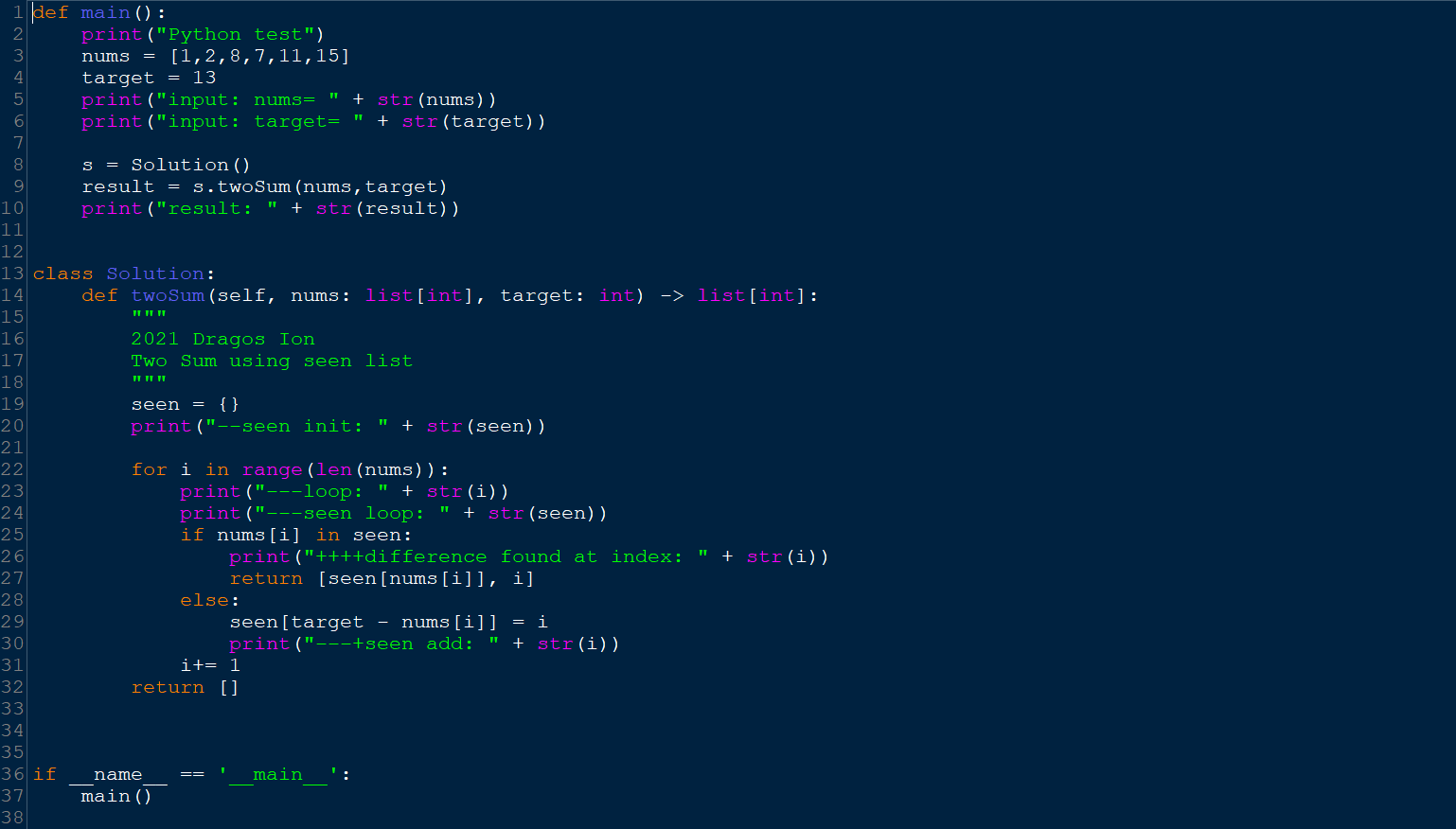
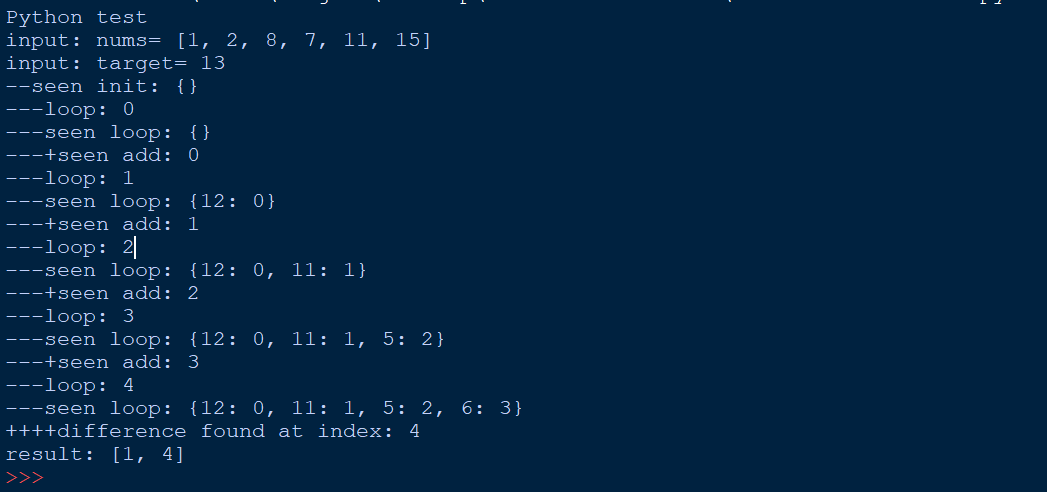
Output Solution code
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: list[int], target: int) -> list[int]:
"""
2021 Dragos Ion
Two Sum using seen list
"""
seen = {}
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] in seen:
return [seen[nums[i]], i]
else:
seen[target - nums[i]] = i
i+= 1
return []








Leave a Reply